5G Downlink Channel Sounding "CSI-RS"

|
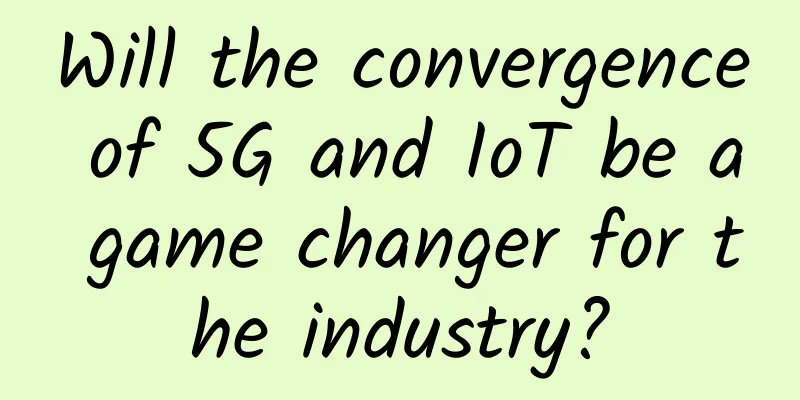
Since 4G, the bandwidth of carriers has increased significantly, from 5M in 3G to 20M. In 5G, the bandwidth of a single carrier has increased to 100M (Sub6G) or 400M (millimeter wave). With such a large bandwidth, the wireless transmission environment changes rapidly, and the attenuation and interference of different frequencies are also different. Without understanding this information, data transmission is just a matter of luck, without prediction and performance guarantee. So, how can mobile phones and base stations keep track of uplink and downlink wireless channel information at any time? Base stations and mobile phones send fixed signals at fixed locations that everyone knows. After both parties receive them, they measure them and find out what changes the spatial transmission has caused to these signals, thereby estimating the channel conditions. The theme of this issue is downlink channel detection. The general process is that the base station sends a reference signal (also called a pilot signal), which is measured by the mobile phone and then sent back to the base station. In this way, the base station can decide how to send data based on the channel quality. 1. Why does 5G use CSI-RS? In the first version (R8) of LTE protocol, the downlink channel condition is completely obtained by the mobile phone's measurement of the Cell Reference Signal (CRS). CRS is evenly spread across the entire LTE carrier bandwidth. Regardless of whether there is any service or not, it takes up resources and continuously transmits signals. It is like a well without a cover in the middle of a highway. All vehicles must go around it, causing serious waste of resources and congestion, and causing continuous interference to neighboring areas. From the above figure, we can see that the CRS of 2 ports (supporting 2x2 MIMO) does not seem to be too much, but the CRS of 4 ports (supporting 4x4 MIMO) occupies more resources. These precious resources could have been used to transmit data, but they are used to transmit CRS of lower value. If 8 ports are to be supported in the future, won't the highway be occupied like a sieve? Therefore, CSI-RS was introduced in the R10 version of LTE. The full name of CSI-RS is Channel State Information - Reference Signal. The name is quite straightforward. This reference signal is used to obtain channel state information. Unlike CRS, CSI-RS is only valid on the bandwidth allocated to the mobile phone, and does not need to be continuously sent on the entire bandwidth. Therefore, even if 8-port transmission is supported, it will not cause a significant increase in system overhead. The network will notify the mobile phone of CSI-RS related information through signaling. If there is no notification, the mobile phone will assume that CSI-RS does not exist. 2. Basic structure and time-frequency characteristics of CSI-RS In the 5G standard, "minimalist design" is its core concept. The "always on" signal that occupies fixed resources, such as LTE's CRS, is naturally abandoned, while CSI-RS is enhanced and expanded for 5G downlink channel detection. As can be seen from the figure above, compared with 4G, 5G has no redundant always-on signals, and the control channel occupies fewer resources, which makes it look cleaner and has higher spectrum utilization. In comparison, the densely packed CRS of 4G is really suffocating. 5G CSI-RS can support up to 32 different antenna ports, each of which is a channel that needs to be detected. The standard allows CSI-RS of multiple antenna ports to be multiplexed on a group of resource elements (RE). The multiplexing methods generally include: Code domain multiplexing: The CSI-RS of different antenna ports actually use exactly the same set of resource elements (REs). The base station and mobile phone multiplex and extract these CSI-RS signals through orthogonal codewords. Frequency domain multiplexing: CSI-RS of different antenna ports actually use different subcarriers within an OFDM symbol. Time domain multiplexing: CSI-RS of different antenna ports actually use different OFDM symbols within a time slot. Different multiplexing methods can be used in combination. The figure above describes a possible 32-port CSI-RS structure, which uses 8 times of code division multiplexing and then 4 times of frequency division multiplexing. Furthermore, the subcarriers may be discontinuous in frequency division multiplexing, and the OFDM symbols may also be discontinuous in time division multiplexing. Generally speaking, the number of resource elements (REs) occupied depends on the number of ports whose CSI-RSs are multiplexed in one RB or time slot. Within the configured CSI-RS bandwidth, CSI-RS can be configured for each resource block (RB), and this mode is called CSI-RS density of 1; or one CSI-RS can be configured for every two resource blocks (RB), and this mode is called CSI-RS density of 1/2. In the time domain, CSI-RS can be configured for periodic transmission, semi-continuous transmission or aperiodic transmission. For periodic transmission, the CSI-RS is repeated every at least 4 time slots and at most 640 time slots. For semi-persistent transmission, CSI-RS will also be configured with a transmission period, but whether it is actually sent depends on the explicit activation of the MAC control source. Once activated, it will continue to send periodically until an explicit deactivation command is received. For non-periodic transmission, the network does not configure the transmission period, but explicitly notifies each CSI-RS transmission through signaling. If the PSDCH scheduled for a mobile phone contains CSI-RS resource units configured for other mobile phones, the mobile phone needs to skip these CSI-RS resource units. However, the mobile phone does not know which resource units it needs to skip, so the protocol designs "zero power CSI-RS" to mark the resource units that the mobile phone needs to skip as zero power CSI-RS. The mobile phone will consider these resource units invalid and skip them directly without any processing. What data can CSI-RS measure? Generally, it includes three items: Channel Quality Indicator (CQI), Rank Indicator (RI) and Precoder Matrix Indicator (PMI). These three items are collectively called Channel State Information (CSI), which is the meaning of CSI-RS. Well, that’s all for this introduction. I hope it will be helpful to you. Thank you very much for sticking with me to the end. |
<<: You want to ask me about the application layer? I'll just talk to you about it.
Recommend
Let's talk about viewing ServiceEntry injection information in Envoy
[[431019]] introduction Istio provides ServiceEnt...
4 ways 5G will change our lives
5G technology is being rolled out in many countri...
Bluetooth, WiFi and Zigbee: Which wireless technology is better?
Wireless technology is all the rage these days! F...
How to quickly develop killer applications? Which will have a greater impact on the market, 5G or edge computing?
[[269430]] Is edge computing the first new trend ...
Hostwinds: VPS/cloud server from $4.99/month, Seattle/Dallas/Netherlands data center, supports Alipay
Hostwinds is a long-established foreign hosting c...
spinservers adds San Jose China Telecom network server, $139/month-Dual E5-2630Lv3/64G memory/1.6T SSD hard disk
spinservers recently sent new product information...
ZJI: 580 yuan/month 2×E5-2630L, 32G memory, 480G SSD, 10M bandwidth, Hong Kong Confederation data center
ZJI is a well-known hosting company in the WordPr...
How to unify heterogeneous networks within a home? 6LoWPAN is a good choice
Part 01 What is 6LoWPAN In order to enable low-sp...
[CyberMonday] DediPath Los Angeles VPS 50% off starting at $10/year, dedicated server starting at $45/month
DediPath has launched a Cyber Monday promotion....
In the 5G era, how do the three major operators fight the edge war?
5G makes the Internet of Everything possible. Whi...
Mid-year review: 10 hottest web startups in 2021
Rising Star If the IT industry has learned anythi...
Wi-Fi chip supply shortage will not be significantly alleviated, and the release of 28nm new production capacity may become the key
According to Electronic Times, industry sources r...
CYUN: 20% off on all VPS, 50% off for old users, Hong Kong VPS monthly payment starts from 14.5 yuan
CYUN is a cloud computing service brand under Hon...
How will the network be reconstructed in the 5G era?
The 5G era is approaching. While people are full ...
The average monthly salary of 5G talents exceeds 14,000 yuan, and Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen are most in need of talent
As 5G commercialization approaches, the demand fo...