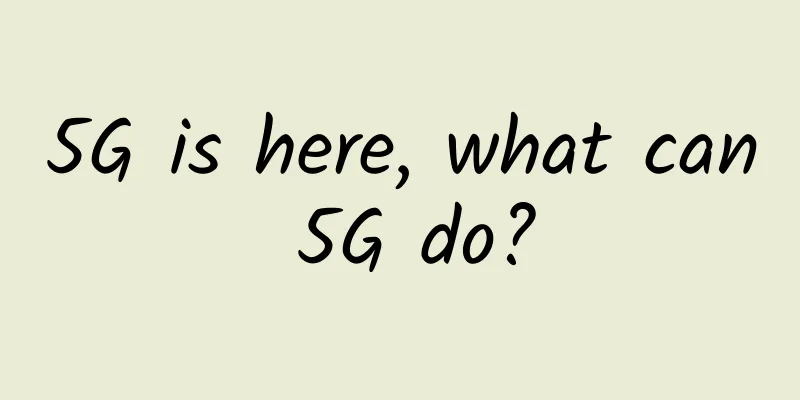How does CDN work? Do you know?

|
A content delivery network (CDN) is a set of servers (also called edge servers) distributed in different geographical locations that can quickly deliver static and dynamic content . Let's take a look at how it works. Suppose Bob, who lives in New York, wants to access an e-commerce website deployed in London. If the request is sent to a server located in London, the response will be quite slow. Therefore, we deploy a CDN server near where Bob lives, and the content will be loaded from the nearby CDN server. The following diagram illustrates this process. picture first stepBob types www.myshop.com into his browser, and the browser looks up the domain name in its local DNS cache. Step 2If the domain name does not exist in the local DNS cache, the browser goes to the DNS resolver to resolve the domain name. The DNS resolver is usually located in the Internet Service Provider (ISP). Step 3The DNS resolver recursively resolves the domain name. Finally, it requests the authoritative name server to resolve the domain name. Step 4If you don't use CDN, the authoritative name server will return the IP address of www.myshop.com. But after using CDN, the authoritative name server will have an alias pointing to www.myshop.cdn.com (the domain name of the CDN server). Step 5The DNS resolver asks the authoritative name server to resolve www.myshop.cdn.com. Step 6The authoritative name server returns the domain name www.myshop.lb.com for the CDN load balancer. Step 7The DNS resolver asks the CDN load balancer to resolve www.myshop.lb.com. The load balancer selects the best CDN edge server based on the user's IP address, the user's ISP, the content of the request, and the server load. Step 8The CDN load balancer returns the IP address of the CDN edge server to www.myshop.lb.com. Step 9Now we finally have the actual IP address we want to access. The DNS resolver will return the IP address to the browser. Step 10The browser accesses the CDN edge server to load content. There are two types of content cached on the CDN server: static content and dynamic content. The former includes static pages, pictures, and videos; the latter includes the results of edge computing. Step 11If the edge CDN server does not have the content in its cache, it is uploaded to the regional CDN server. If the content is still not found, it goes up to the central CDN server or even to the origin - the London network server. This is called a CDN distribution network, where servers are deployed geographically. How to prevent videos cached on CDN from being pirated?
Encryption: Encrypt the video file so that only authorized clients can decrypt and play it. Standard encryption algorithms such as AES can be used. Dynamic Watermark: Add traceable dynamic watermarks to videos, which change as the video plays, allowing the pirated version to be traced back to its source.
Use signatures and tokens to ensure that each request is authenticated. For example, add a timestamp and cryptographic signature to the video link to ensure that it is only valid within a specific time period and that unauthorized requests are rejected.
Set a shorter cache expiration time to avoid long-term storage of video content on CDN nodes. By controlling TTL (Time To Live) or cache clearing strategy, the cache survival time of the video can be reduced, thereby reducing the risk of piracy.
Configure CDN and servers to restrict the sources of access to video content. For example, use HTTP Referer header check to ensure that only requests from legitimate websites or applications can access the video. |
<<: Telecommunications industry survey: AI will become the top investment area in 2025
Recommend
5 web trends you need to know about in 2021
On December 14, 2020, a massive network outage ca...
CloudCone: Large hard disk VPS annual payment starts at $17.77, Los Angeles MC data center, KVM architecture
CloudCone is a foreign hosting company founded in...
China Unicom begins deploying 2G network and stops all services
2G outdated communication technology will inevita...
Explain RPC and HTTP in plain language
With the continuous development of enterprise IT ...
Building a cloud foundation to connect the world | Ruijie Networks presents cutting-edge products at the 2021 PT Expo
On September 27, 2021, the 30th China Internation...
8 technologies that are changing IT services
No one can deny that service is a job performed b...
[11.11] Maxthon consoles are 32% off, top up 611 yuan and get 111 yuan for free
Aoyo Host (aoyozhuji/aoyoyun) has launched this y...
6G network, what application scenarios will it have in the future?
Looking back at the entire development history of...
In the first half of the year, the number of Internet users in my country reached 940 million, and the number of active IPv6 users reached 362 million.
Yesterday, the China Internet Network Information...
The overlooked hardware vulnerabilities in enterprise networks
Typically, hackers will gravitate to the weakest ...
Network management benefits! Several difficult problems and solutions for LAN
As a qualified network administrator, I believe t...
Unlocking the shackles of 5G network development: Cloud-native NFV is indispensable
The implementation of 5G technology will bring th...
Summary information: Tianshang Cloud/KuaiKuai Network/Asia Cloud/Cool Cloud/Qingyun Internet/PIGYun
In early May, I received a lot of product or Labo...
VMISS 30% off, Hong Kong CN2/Korea CN2/US CN2/Japan IIJ monthly payment starts from 3.5 Canadian dollars
VMISS is still offering a 30% discount this month...
DiyVM: 50 yuan/month-2GB/50GB/5M/Hong Kong CN2 line
DiyVM is a brand of Hong Kong Ruiou International...




![[11.11] UFOVPS 30% off, top up 200 yuan and get 20 yuan, Japan/Hong Kong CN2 GIA/US high defense optional](/upload/images/67cabd2788c2b.webp)