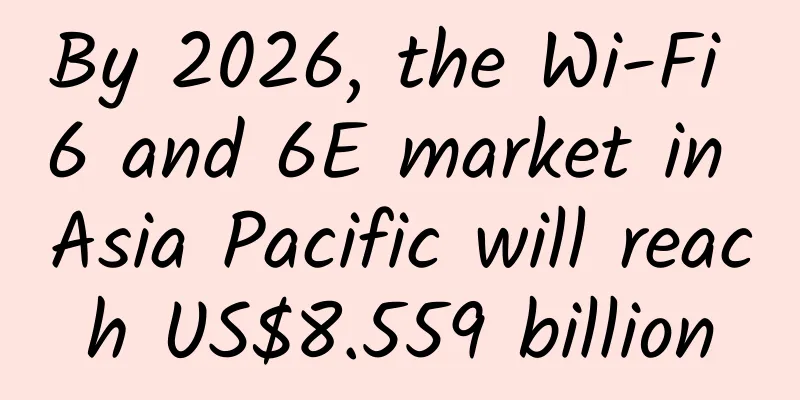What should you consider before looking for an SD-WAN provider?

|
SD-WAN supports use cases across a variety of vertical industries, and essentially any organization with a distributed structure can benefit from the technology.
Before choosing a specific SD-WAN technology, it is important to evaluate your current branch network requirements. There are many ways to purchase the technology, from fully self-service to relying on the SD-WAN vendor for comprehensive management services. Pricing options for SD-WAN deployments are complex and can range from options to purchase the appliance, licenses to run the software on your own servers, or software that runs via subscription. How SD-WAN Technology Meets Business Challenges As with all IT projects, it’s best to start with the problem you’re solving and the business value it brings to the organization. For SD-WAN, the problem may be specific to an application, such as Office 365 performance, poor WAN connection reliability, VoIP quality, or the sheer volume of WAN traffic resulting from video transmission. Business challenges may also be more general, with demand for WAN bandwidth at office locations growing faster than the enterprise WAN bandwidth budget. Another business case may be related to IT agility. For example, there is a requirement to quickly deploy a temporary branch office, such as a construction site or a temporary retail store. The following are examples of special development area network use cases for specific problems: Hybrid WAN . SD-WAN technology supports the deployment of hybrid WAN, especially the ability to use two or more WAN links to provide enhanced bandwidth and reliable connections for each remote branch. Typical hybrid WAN deployments allow organizations to add high-speed Internet connections to existing MPLS branch networks. Through application prioritization and traffic load balancing, SD-WAN can ensure that critical applications have the best links available at all times. Based on the excellent performance and economic benefits of Internet links, hybrid WANs are generally easily accepted by the public. Branch reliability . Related to the hybrid WAN use case, branch communications reliability can be enhanced by deploying two or more WAN connections using SD-WAN. Organizations such as banks, restaurants, and retail stores can experience a huge impact on their business when their branch offices are offline during their business hours, most directly resulting in loss of revenue. Other verticals point to the loss of user productivity when branch communications are unreliable. For example, there may be a critical business issue where an executive within the enterprise is unable to access critical applications and information due to a failed access. Branch security . Security requirements for branch offices can vary widely, depending on the applications used, the vertical industry, and specific regulatory and compliance requirements. Industries such as finance, public safety, healthcare, and retail are all subject to specific security regimes. SD-WAN vendors’ technology provides enhanced security for relatively insecure internet links and interoperates with existing network security infrastructure, such as firewalls at branch offices or centralized locations. Unified Communications (UC) . Enterprise communications services, including VoIP and video, require specific network capabilities to deliver a high-quality user experience. UC requires WAN connections with adequate bandwidth, low latency, and minimal packet loss. SD-WAN enables organizations to prioritize UC communications over WAN links, monitor UC communications performance, and adjust the network based on IT needs to improve quality. In hybrid WAN use cases or internet-only links, SD-WAN can fix the unpredictable bandwidth issues of the internet. Each of the leading SD-WAN vendors has its own proprietary approach for application identification and traffic prioritization to improve UC quality. Temporary sites . Branch office locations can change regularly, wherever they are part of normal business projects, such as new construction sites; new or changing store locations; changes due to mergers and acquisitions of companies. SD-WAN enables IT teams to quickly deploy WAN connectivity to new locations in a matter of days. Using SD-WAN’s zero-touch deployment and centralized management, IT can send an application to a location and have untrained personnel connect that box to the internet or 4G LTE. Remote devices can be remotely configured by central IT resources. Remote and mobile locations . Many organizations have teams that maintain critical applications in small or remote locations. For example, those responsible for public safety have truly mobile IT processes. SD-WAN can be deployed as part of a remote access service to facilitate employees working from home. It can provide secure connectivity and improve the performance of critical applications. Services from SD-WAN vendors offer 4G LTE links to provide true high-speed connectivity to mobile sites. As more IT applications are distributed at the edge, such as the Internet of Things, the remote and mobile capabilities of SD-WAN are becoming increasingly important. WAN architecture . The WAN provides critical connectivity between remote branch offices and central locations. It also enables remote workers to access cloud-based applications such as Office 365; UC; remote computing and storage services, such as Amazon Web Services or Google; and professional applications, such as Salesforce. The growth in the number of UC and cloud-based applications continues to put pressure on bandwidth and latency in many distributed enterprises. Here are some preliminary questions about SD-WAN architecture that organizations should ask when analyzing their WAN’s current and future needs:
What SD-WAN technology capabilities are needed? SD-WAN technology includes a comprehensive and growing catalog of capabilities. IT organizations should evaluate their specific requirements when researching the SD-WAN market. Here are some questions to help organizations evaluate SD-WAN capabilities:
SD-WAN Purchasing Options Organizations can choose to install and manage SD-WAN technology themselves or outsource some or all of the process. Network resellers, managed service providers, and communications service providers can assist with SD-WAN implementation. Organizations should carefully evaluate their internal capabilities and costs compared to external managed resources. SD-WAN vendors offer a wide range of options when it comes to choosing a specific SD-WAN implementation. Compared to choosing a managed service provider, organizations implementing SD-WAN in-house have three main options:
As a technology, SD-WAN has the ability to address a wide range of WAN challenges, solving for use cases, vertical industries, and geographies. Before you begin evaluating SD-WAN vendors, it’s important to prioritize your specific business challenges and answer a series of questions about your WAN environment. |
<<: Multi-access Edge Computing – Part 1: How does Multi-access Edge Computing work?
Recommend
5G may be just around the corner as a universal core for fiber
Convergence between wired and wireless networks i...
Lenovo Debuts at Microsoft IoT Conference, Driving Business Intelligence Innovation with Smart IoT Devices
On December 3, the highly anticipated 2019 Micros...
Operators competing in the digital service market for SMEs are facing opportunities for transformation and development
Recently, the Ministry of Industry and Informatio...
The new EMUI system supports Huawei Enjoy 10S to bring a smart entertainment experience to a thousand-yuan phone
Nowadays, watching dramas, movies, new shows, and...
Where is the entrance to 5G message service? You may not think of it
Since the Ministry of Industry and Information Te...
What is the difficulty in porting your number?
Number portability was once considered an importa...
5G cybersecurity market to reach $16 billion by 2028
The 5G network security market is expected to gro...
How to build a secure HTTPS site step by step
[[261093]] Usually a web site opens HTTPS. Taking...
Today's encryption mechanisms will be defeated by quantum attacks, except for generalized knapsack codes.
[51CTO.com original article] Today's encrypti...
Juniper Networks 2017 Annual Conference grandly held, focusing on telecom and OTT markets
[51CTO.com original article] In February 2017, th...
Understand in one article how the intranet and extranet communicate?
For network developers, we often use TCP and UDP ...
5G Thinking | Moderately Advance 5G Network Construction
Network construction is the cornerstone of 5G com...
The long-awaited 5G messaging trial will be launched in late October or early November
"China Unicom and China Telecom are working ...
Learn the network protocol stack in ARM-uboot from scratch
[[401440]] Network protocol stack in uboot The ne...
Ma Zai Comics: How to "wave four times" to your girlfriend
[[357361]] This article is reprinted from the WeC...


![[Black Friday] AlphaVPS: AMD Ryzen series from €15.99/year, large hard drive VPS from €19.99/year, Los Angeles/Germany/Bulgaria data centers](/upload/images/67cabcce4ecf1.webp)