Example: How to plan IP addresses for a large-scale monitoring network system?
|
For monitoring projects, many faults are caused by improper IP address settings, such as IP conflicts, or several monitoring images not being displayed, etc., which are all related to IP. It is very important to allocate IP addresses reasonably. 1. Why should IP be allocated reasonably? For small monitoring projects, the IP address setting is relatively simple and most people will not make mistakes. However, for monitoring projects with more than 254 points, it is easy to make mistakes. Why?
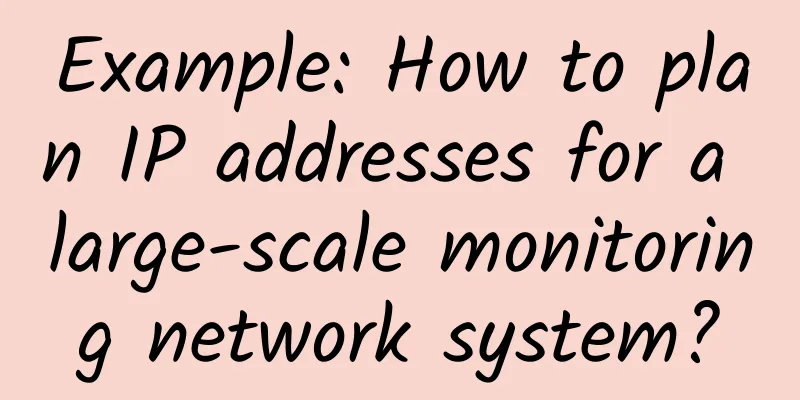
So what should we do? Dividing the network segments is a reasonable approach. 2. How do large networks allocate IPs? For monitoring of more than 254 points, although we can assign IP addresses without dividing the network segments, a good network planning is not only about simply and barely realizing the functions, but also needs to focus on the later maintenance and the clarity and scalability of the entire network. Let's take an example to see how to assign IP addresses. A factory monitoring project is divided into four areas with a total of 300 points. All equipment is in an intranet, and the main line is connected by optical cable. There are two areas with 70 points each, and the other two areas with 80 points each. How to set their IP addresses? The allocation is as follows: First of all, there are two ways to monitor these 300 points: The first type: No VLAN division, all arranged in a large network segment The first method is to not divide VLANs and use layer 2 switches. The IP address can be directly set to an IP address range of 192.168.0.1-192.168.1.254, and a subnet mask of 255.255.254.0. A total of 500 IP addresses can be used, all of which are accommodated in a large network segment, which is completely sufficient. This large network segment includes two IP segments:
There are 508 IP addresses in total, which is more than enough. Some friends may wonder how the subnet mask 255.255.254.0 is derived, and why it is not 255.255.255.0? Subnet mask calculation: Here we will explain the IP address range 192.168.0.1-192.168.1.254 separately. Why is the subnet mask of this network segment 255.255.254.0? This IP address range includes two IP segments.
In layman's terms, their common subnet mask is 255.255.254.0. Many small and medium-sized monitoring projects are intranets. In many cases, there is no need to divide VLANs for intranet projects, which can save resources. However, in order to prevent network storms, port isolation can be used to ensure network security. The second method: divide VLAN For large-scale monitoring, VLAN division is the preferred method. Here we focus on the method of dividing network segments. Using switches can directly divide the network into four segments. Main monitoring address: 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Each network segment can accommodate more than 250 points, and there are a total of 1,000 IP addresses available in the four segments, which is more than enough to allocate IP addresses to each area. In addition, if additional points are added in each area in the future, there will be sufficient reserves. It is worth noting that the access layer switches here need to be reasonably allocated and selected. So what are the benefits of dividing network segments in this way? The IP addresses of the four areas are relatively obvious. If there is a problem with a camera, you can quickly locate the camera with the problem by batch pinging the IP addresses. At the same time, it can also effectively prevent IP conflicts. IP is a problem that occurs frequently in network failures, and it can also reduce broadcast storms. |
<<: Comparison of LPWAN technologies: Ten criteria for successful implementation
>>: Most enterprise networks cannot handle big data loads
Recommend
China Mobile launches A-share listing: "Making money" but not "cutting leeks"
On the evening of May 17, World Telecommunication...
V5.NET: 30% off for first order from new customers, Hong Kong E5 server as low as HK$385/month
V5.NET is a business that provides independent se...
Attention to those whose phone numbers begin with 13, 15, 18, etc.! There may be a big problem with your data plan!
Users whose mobile phone numbers begin with 13, 1...
Several secrets to protect cabling in green data centers
At present, the degree of enterprise informatizat...
What security risks may cause the Internet speed to suddenly slow down?
[[434023]] This article is reprinted from the WeC...
Everyone is promoting 5G products and 5G phones. Is 5G really that good? Should I choose a 4G or 5G phone?
The word 5G is "very hot". The topic of...
Better connections enable faster, more flexible networks
For the past two decades, network architectures h...
Protecting corporate intranet data security in just seven steps
In the Internet information age, science and tech...
China's AI market is undergoing another major change. First-line AI+ cloud network security services are ready to go
Recently, China's AI market has undergone tre...
DesiVPS: San Jose VPS starts at $18.99 per year, 1GB/25GB/1Gbps unlimited data
DesiVPS previously provided VPS hosts in Los Ange...
Global semiconductor industry capital expenditure will reach nearly $150 billion in 2021
[[426618]] On the 29th, the Semiconductor Industr...
How can operators tap into the 5G dividend when they have over 600 million 5G users?
Currently, the 5G era is accelerating towards us....
The number of terminal connections has exceeded 200 million, and 5G commercial use still needs to break through
Recently, data released by the Ministry of Indust...
Is your phone stolen within minutes after you lose it? Teach you how to set the SIM card password
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technolo...
"Number Portability" has been officially launched! Netizens complain: The operators are full of tricks!
Some time ago, the Ministry of Industry and Infor...
![[6.18] iOVZ VPS 20% off monthly payment and 30% off annual payment, Hong Kong VPS gets double memory](/upload/images/67cabe6619e38.webp)








